NEW! Students’ Practical Training - I-st semester of 2022-2023 academic year
Core clinical teaching facilities must be provided in a veterinary teaching hospital (VTH) with 24/7 emergency services at least for companion animals and equines. Within the VTH, the Establishment must unequivocally demonstrate that standard of education and clinical research are compliant with all ESEVT Standards, e.g. research-based and evidence-based clinical training supervised by academic staff trained to teach and to assess, availability for staff and students of facilities and patients for performing clinical research and relevant QA procedures. For ruminants, on-call service must be available if emergency services do not exist for those species in a VTH.
The Establishment must ensure state-of-the-art standards of teaching clinics which remain comparable with or exceeding the best available in the private sector.
The VTH and any hospitals, practices and facilities (including EPT) which are involved with the curriculum must meet the relevant national Practice Standards.
On the basis of the Interdepartmental clinic of horses, ruminants, pigs, small and exotic animals (VTH) there is an ambulance car, which is designed for emergency trips regardless of the time of day. The car is equipped with surgical and obstetric sets of instruments and medicines (anti-shock, analgesic, antispasmodics, rehydration therapy drugs, means for maintaining the cardiovascular and respiratory systems). The visiting team includes a doctor on duty at the clinic and 2-3 students.
During clinical training, students provide veterinary care to animals under the guidance of a teacher. When conducting classes in the clinic, students are dressed in protective suits (according to requirements). Each student's overalls have a badge with the full name in Ukrainian and English. Before each lesson with animals, students are instructed in safety. The main clinical training since 2018 is conducted in the training veterinary hospital. The hospital staff is represented by the head and five resident doctors. The basic clinical training in the clinic is provided by academic staff in the areas of specialization - diagnostic imaging, anesthesiology and surgery, reproductive medicine, internal metabolic diseases, ophthalmology, intensive care,
preventive medicine. The duty in the clinic is according to the schedule approved by the dean's office. The clinic works 24/7. The emergency services for pets, horses, ruminants and pigs are available by telephone.
However, in all cases, in the presence of patients in inpatient treatment, alternation is mandatory. Preliminary acquaintance of students with work of clinic, safety instructions, procedures and logistics is carried out. The rotation of students begins with the registration of patients, the study of their anamnestic data and the initial clinical examination with the participation of a doctor, which is reported to the teacher. If necessary, additional diagnostic procedures are assigned in which the student participates. During the free time the student analyzes this and similar clinical cases, which he discusses with the teacher. The student's responsibilities also include registering patients, entering all relevant data into the electronic database and filling in his / her protocol. At the end of the working day, the students on duty discuss all clinical cases during the day, and the teacher evaluates their work.
Students work in a similar way in outpatient clinics. In the aggregate of the results of students' work in clinics, which are stored in the electronic database, the student is credited or not credited with one or another indicator of his clinical training.
Types of specialized care provided by clinics
|
Сlinics |
Specialized care |
|
Horses |
Internal medicine, surgery (including orthopedics, trauma surgery, anesthesia), dermatology, ophthalmology, dentistry, obstetrics and gynecology, andrology |
|
Small animals |
Internal medicine (including cardiology), surgery (including orthopedics, endoscopic surgery, traumatic surgery), anesthesia, dermatology, oncology, physiotherapy, ophthalmology, reproduction |
|
Small mammals, reptiles, birds |
Internal medicine and surgery, diagnostic imaging in small mammals, reptiles, ornamental birds |
|
Cattle |
Internal medicine, surgery, orthopedics, obstetrics, gynecology, andrology |
|
Pigs, small ruminants |
Internal medicine, surgery, orthopedics, reproductive medicine of pigs, small ruminants (sheep, goats) |
During the holidays, the clinics are staffed by teachers and students on a volunteer basis. If there are patients in accordance with the current topics of the educational process in a particular discipline, subgroups of students (4-8 people per teacher) are involved in the work of the clinic.
The Establishment must ensure that students have access to a broad range of diagnostic and therapeutic facilities, including but not limited to: diagnostic imaging, anaesthesia, clinical pathology, intensive/critical care, surgeries and treatment facilities, ambulatory services, pharmacy and necropsy facilities.
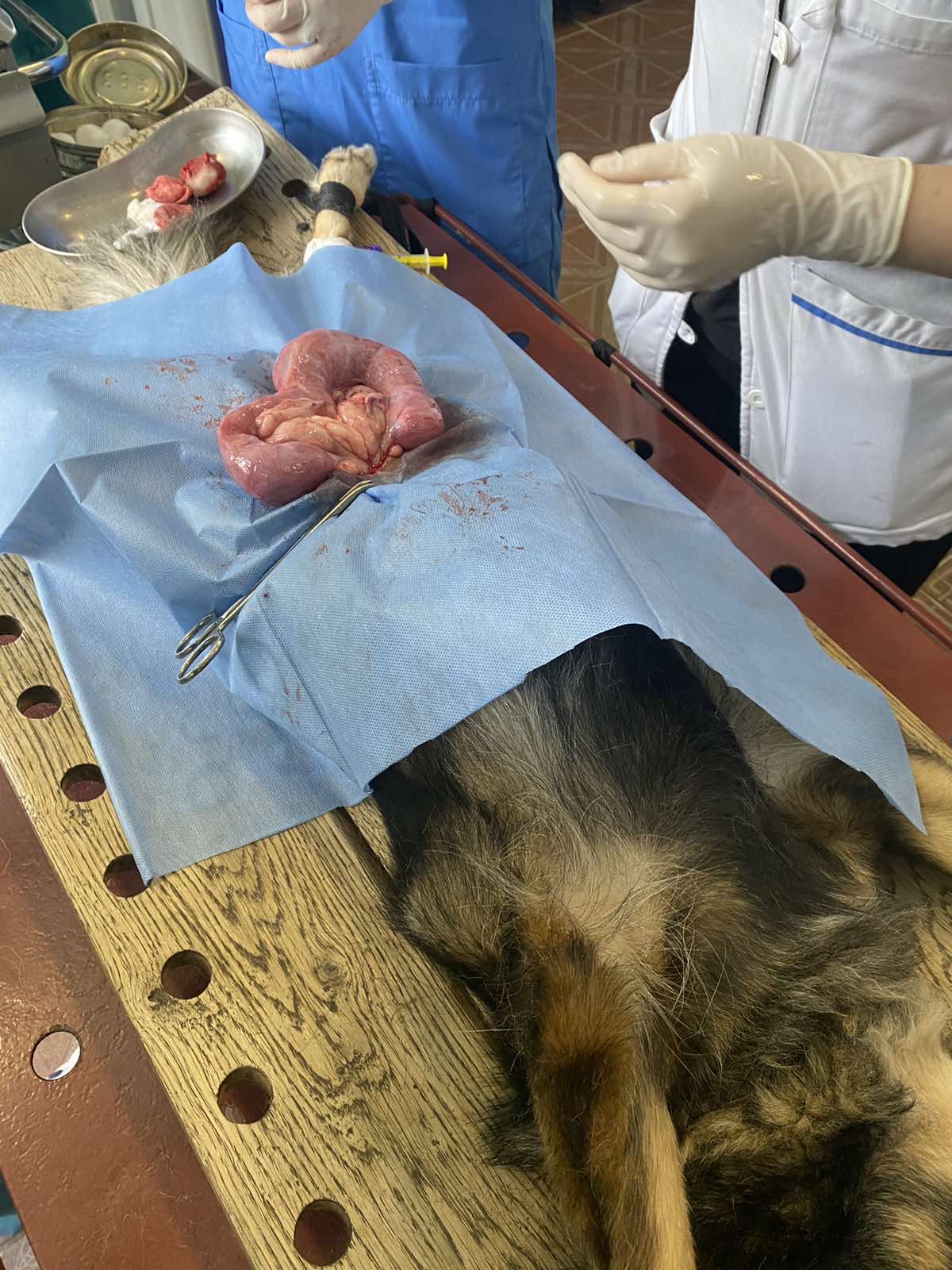
Students have access to a wide range of diagnostic and therapeutic tools. In the process of learning, students develop skills in diagnosing various pathologies using special devices and equipment: patient monitor, X-ray machine (stationary and mobile), ultrasound machine, laparoscopy, ophthalmoscopy, biomicroscopy of the eye and various methods of laboratory diagnosis. During surgery, students have access to anesthesia techniques and operations on animals. They have the opportunity to provide emergency care under the supervision of a teacher. When studying the discipline "Clinical Pharmacology" and during the duty in the clinic, students study the organization of the veterinary pharmacy. They participate actively under the supervision of teachers in conducting necropsy procedures. All procedures must be formalized in a protocol, discussed with the teacher with the participation of other students and animal owners. Mastering the relevant procedures should be recorded in the journal of progress and record book of clinical skills.
Appropriate isolation facilities must be provided to meet the need for the isolation and containment of animals with communicable diseases. Such isolation facilities must be properly constructed, ventilated, maintained and operated to provide for animal care and for prevention of spread of infectious agents. They must be adapted to all animal species commonly handled in the VTH.
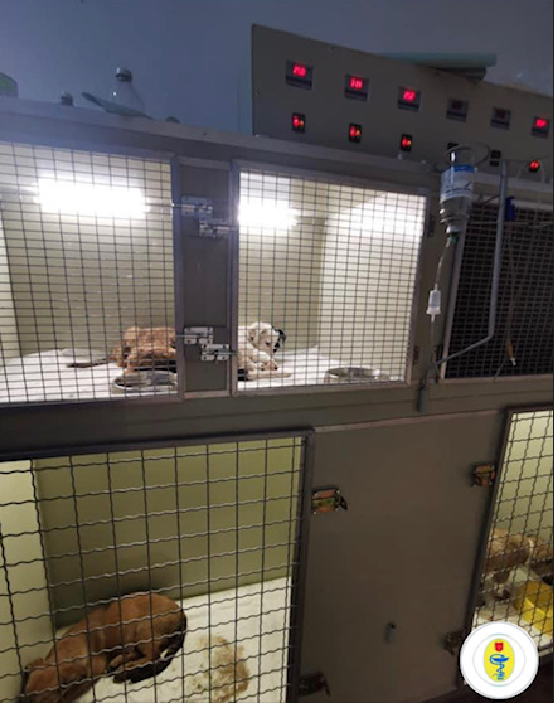
For the safe treatment of infectious and infection suspected animals on the campus of the faculty, namely, next to the Interdepartmental veterinary clinic (VTH) there are isolator on cells. Their presence makes it possible to control infections and prevent threats to humans, animals and the environment.
Infirmary is sufficient for the usual mode of clinics, correspond (in number of places) for animals to usual loading. Infirmaries for horses, large and small ruminants, pigs are arranged in separate rooms. The infirmary for dogs and cats is located in the same building, has common facilities for students on duty and storage of medicines. All infirmaries follow measures to isolate and prevent the spread of infectious diseases: entrances for animals and staff are separated, there are separate passages. Animals enter the infirmary through a special door or gate, the size of which corresponds to the type of animal and allows in case of death of animals to evacuate it from the room. The infirmaries are supplied by autonomous ventilation. Faeces and waste are removed from the storage tanks, where they are disinfected and removed to the biowaste site.
The pathways of animals of different species do not intersect directly, which is the transmission of pathogens through fomites. Staff and students enter detention facilities through biosafety barriers, which are equipped with hygienic units, changeable footwear and clothing, and personal protective equipment. The premises are equipped with means for washing and cleaning of premises, care items, places for their storage, places for storage of fodder and medicines, disinfectants.
Isolators for dogs and cats in the clinic are the busiest and are used for inpatient treatment of infectious and sick animals.
Compliance with the rules of biosafety in infirmaries is supported by authorized staff (doctors) and teachers. Students undergo introductory and current instruction on the rules of work in isolation wards. The isolators have a system of visualization of biosafety rules with the help of special signs and explanations available for perception and understanding.
Keeping animals in an infectious hospital

Extramural clinical practice to acquire practical skills and competencies
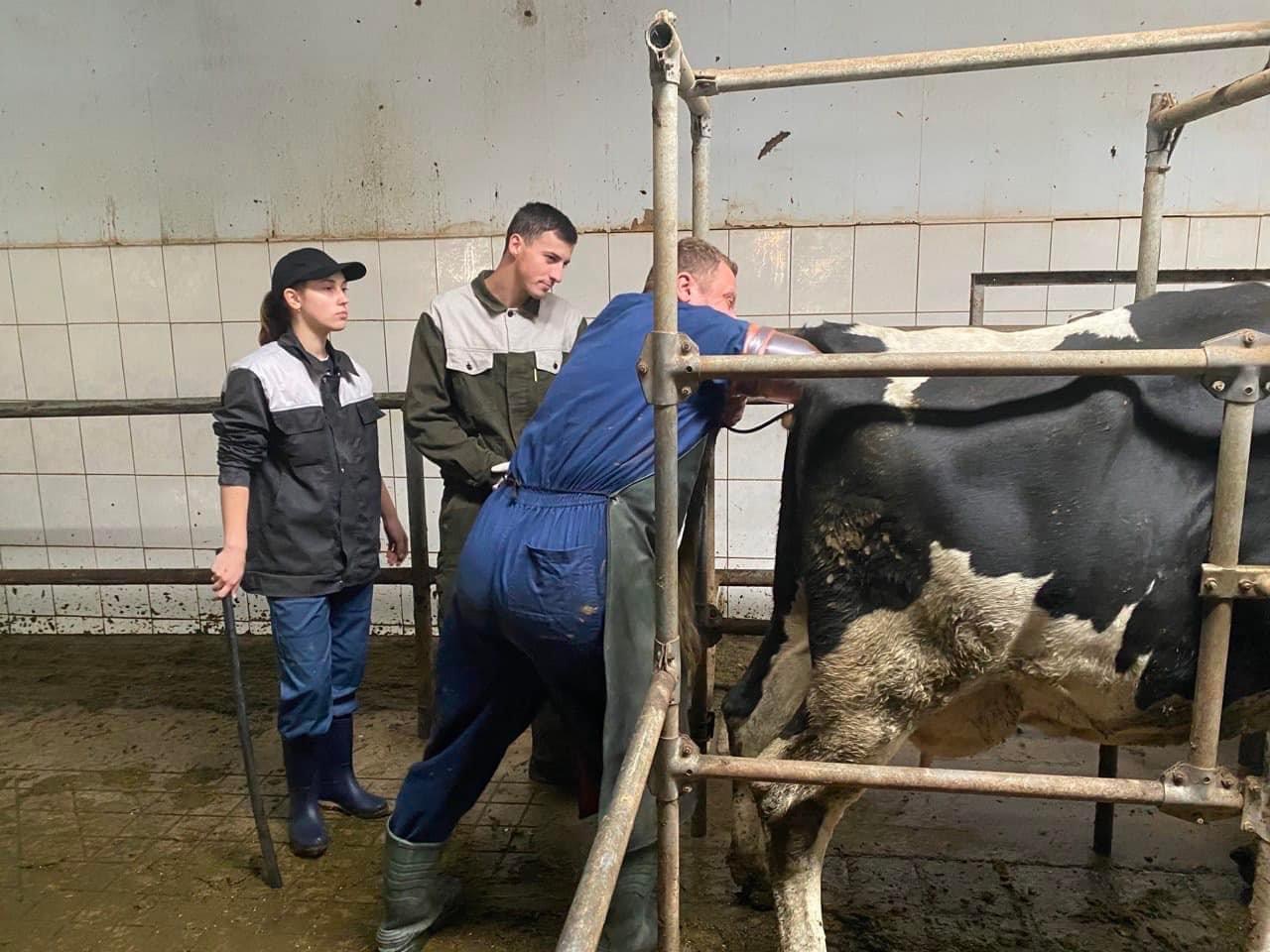
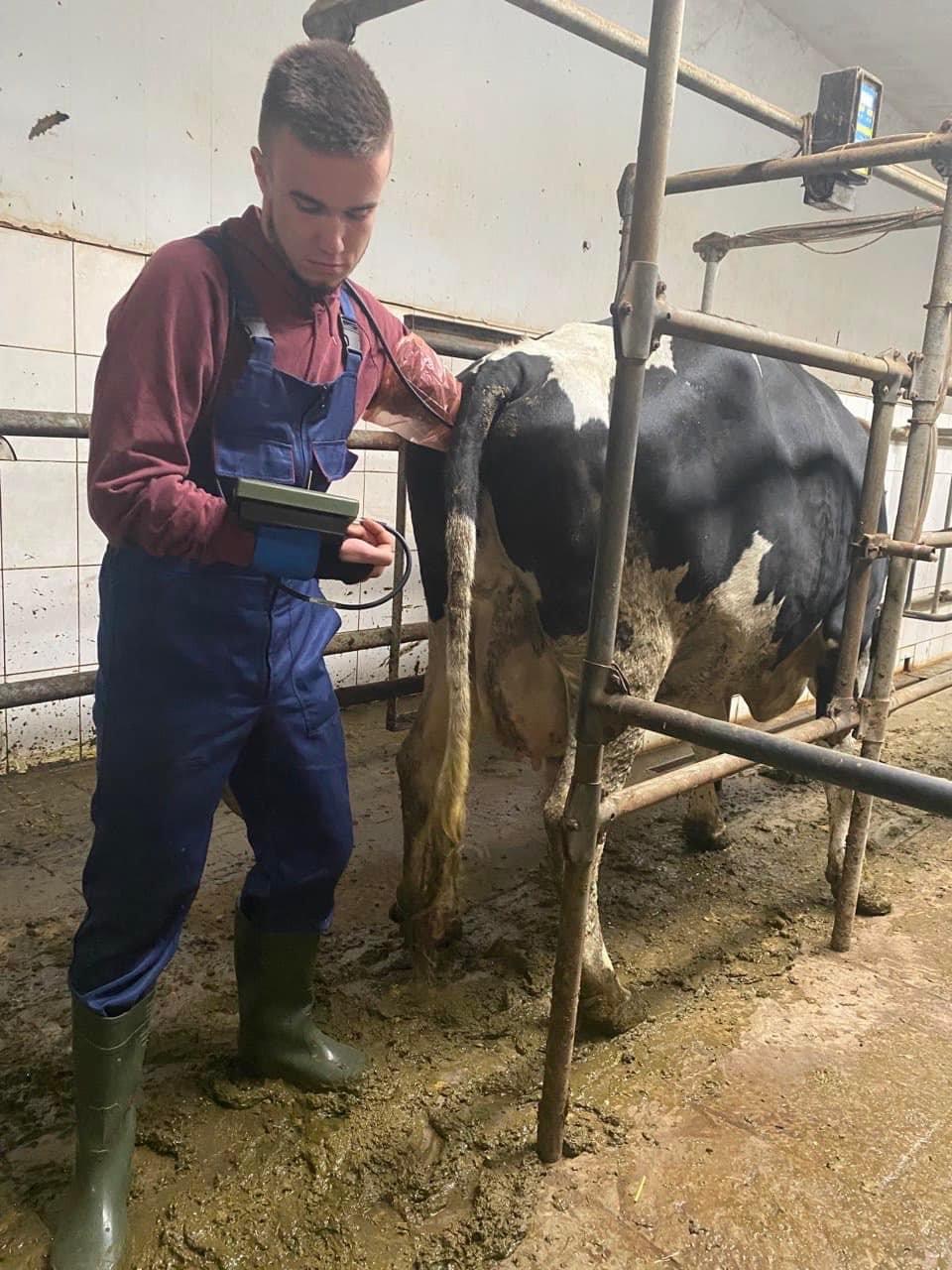
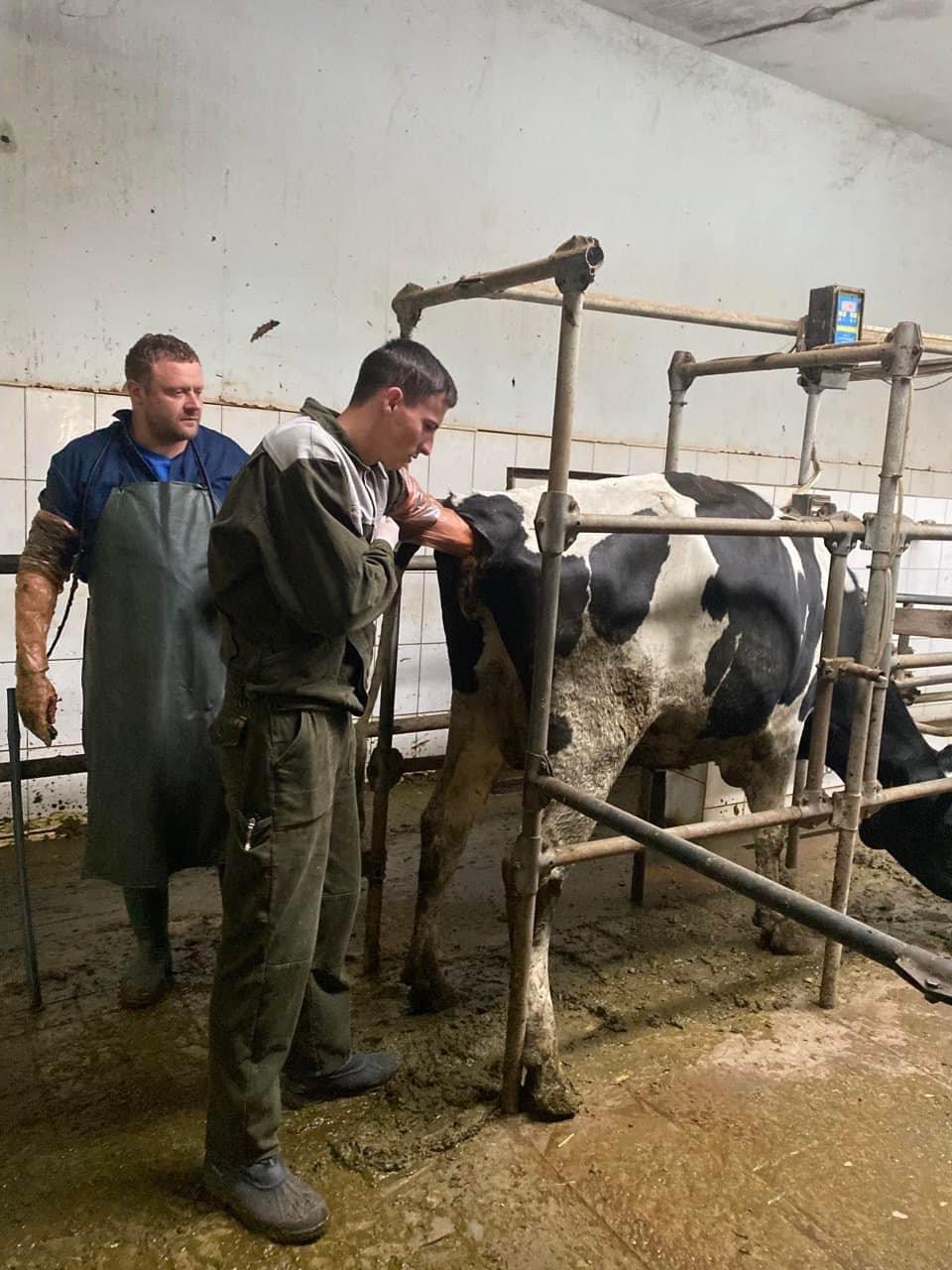
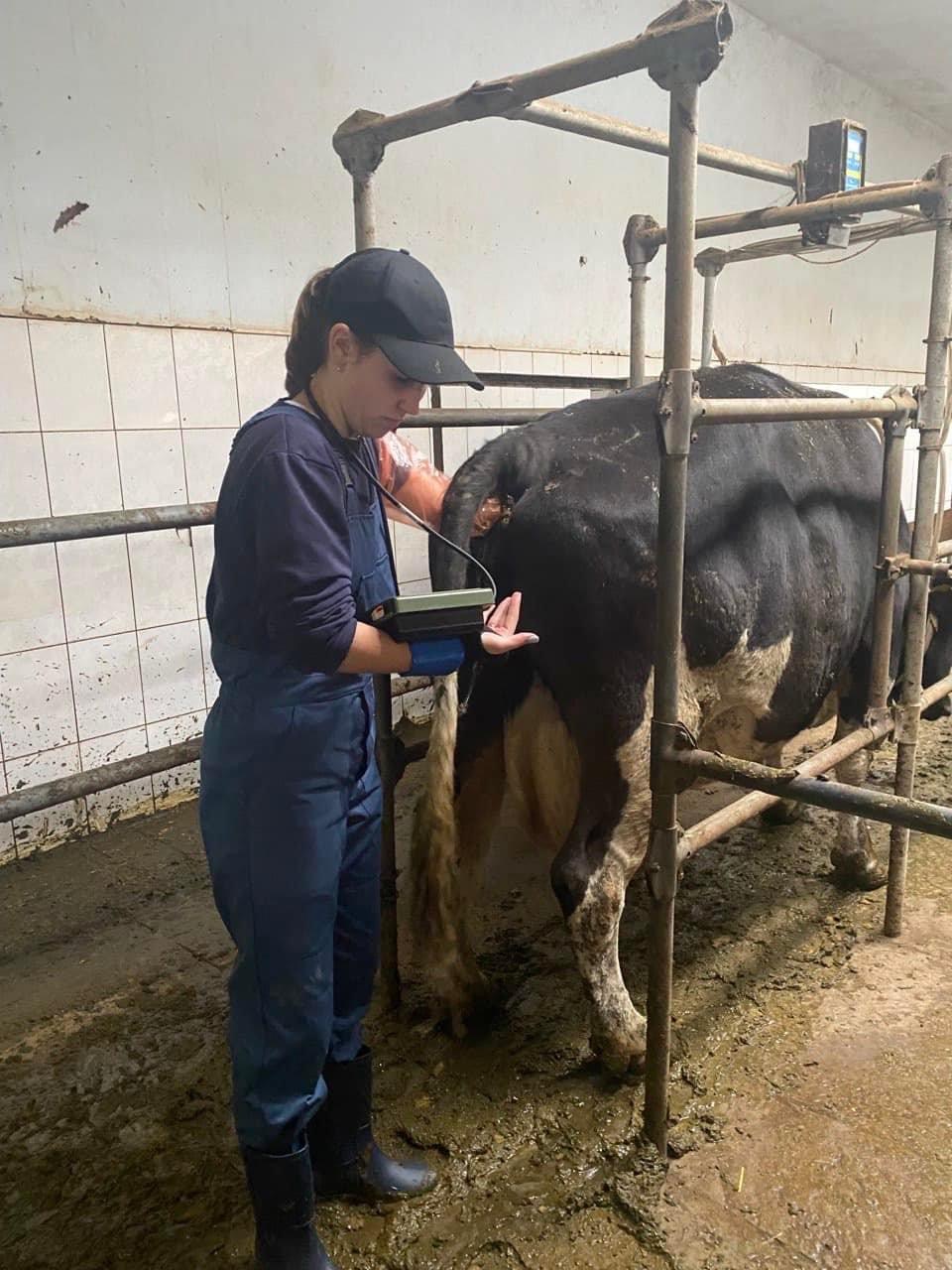
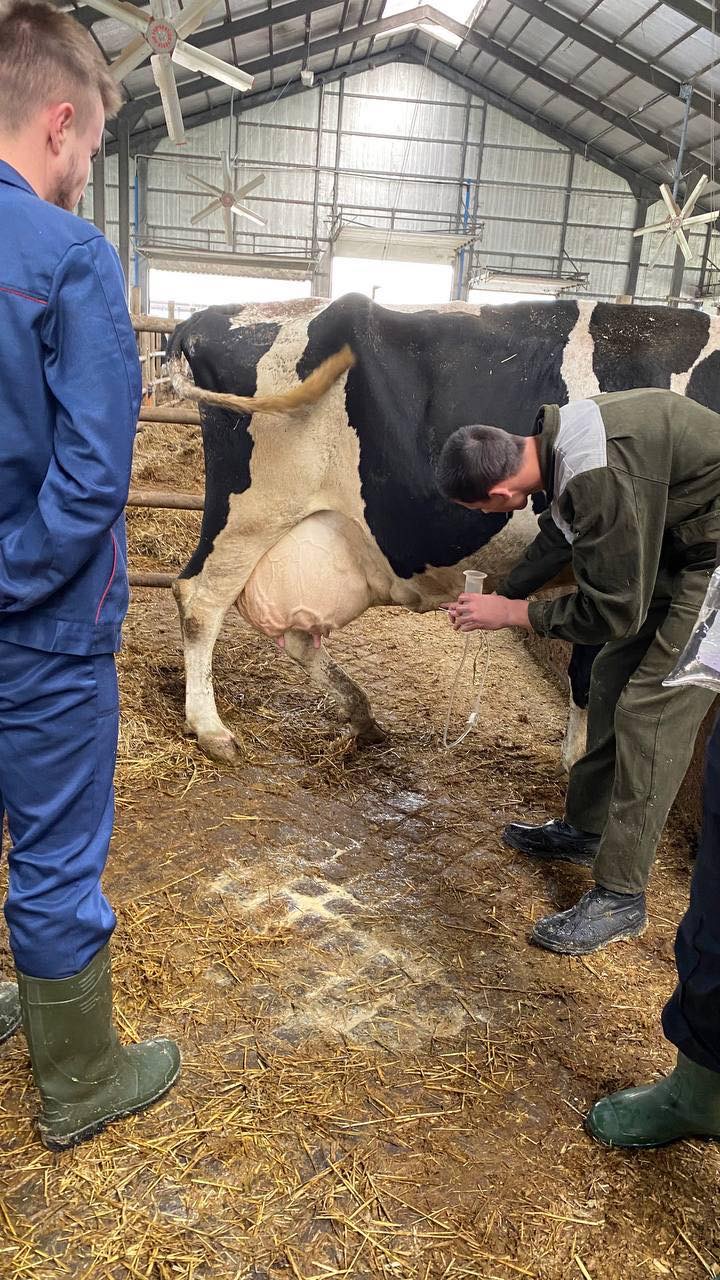
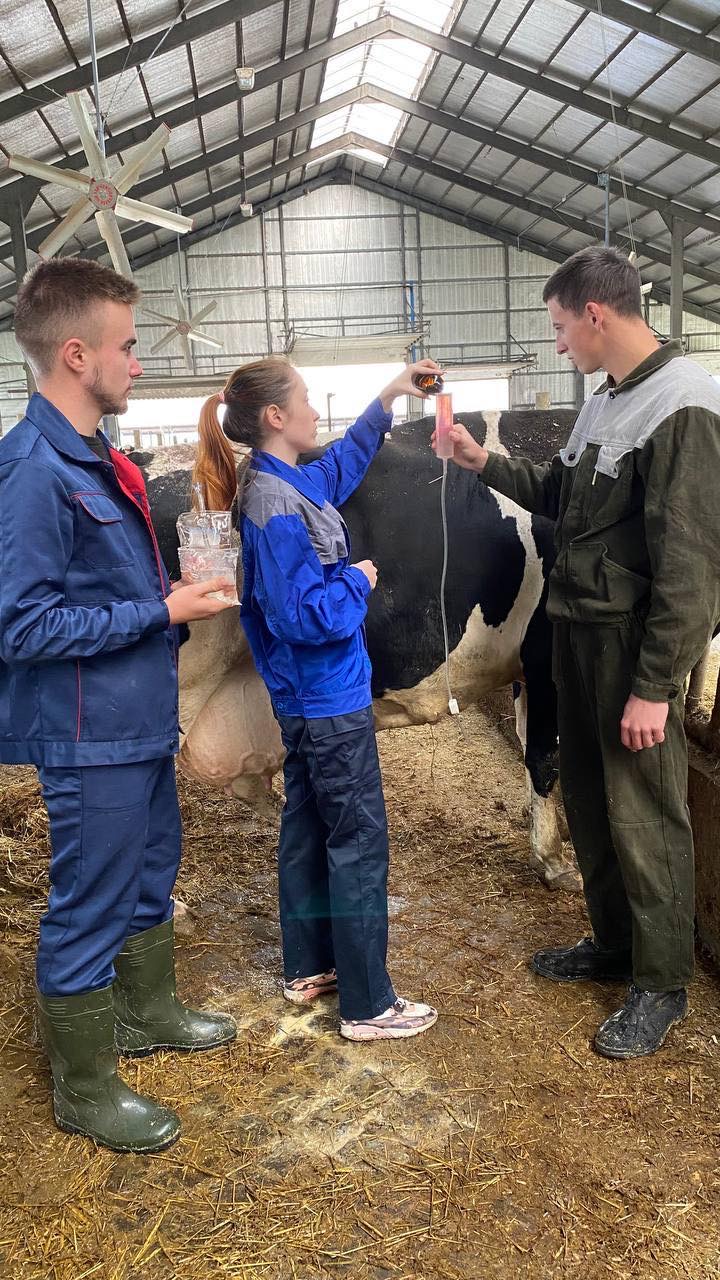
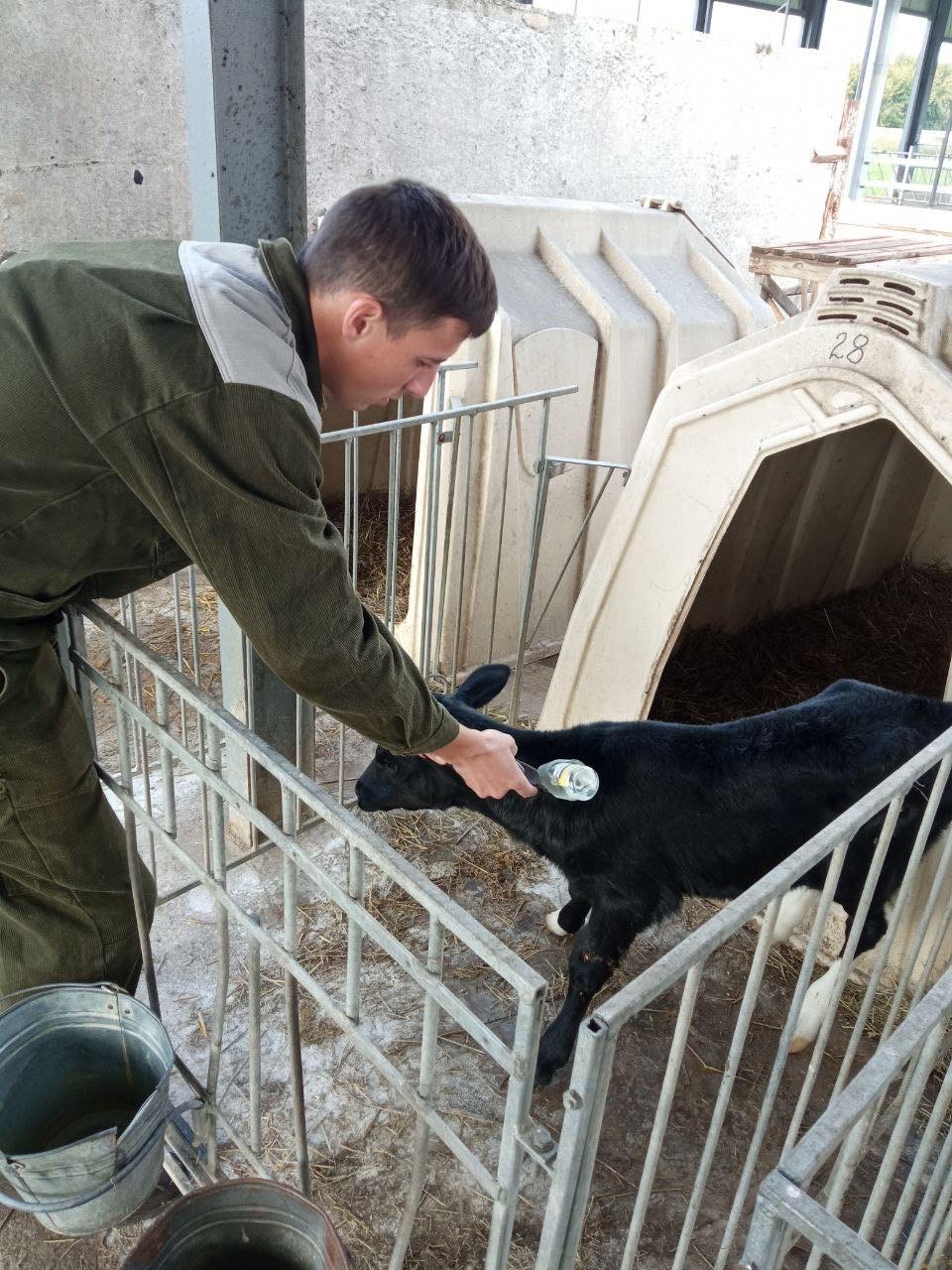
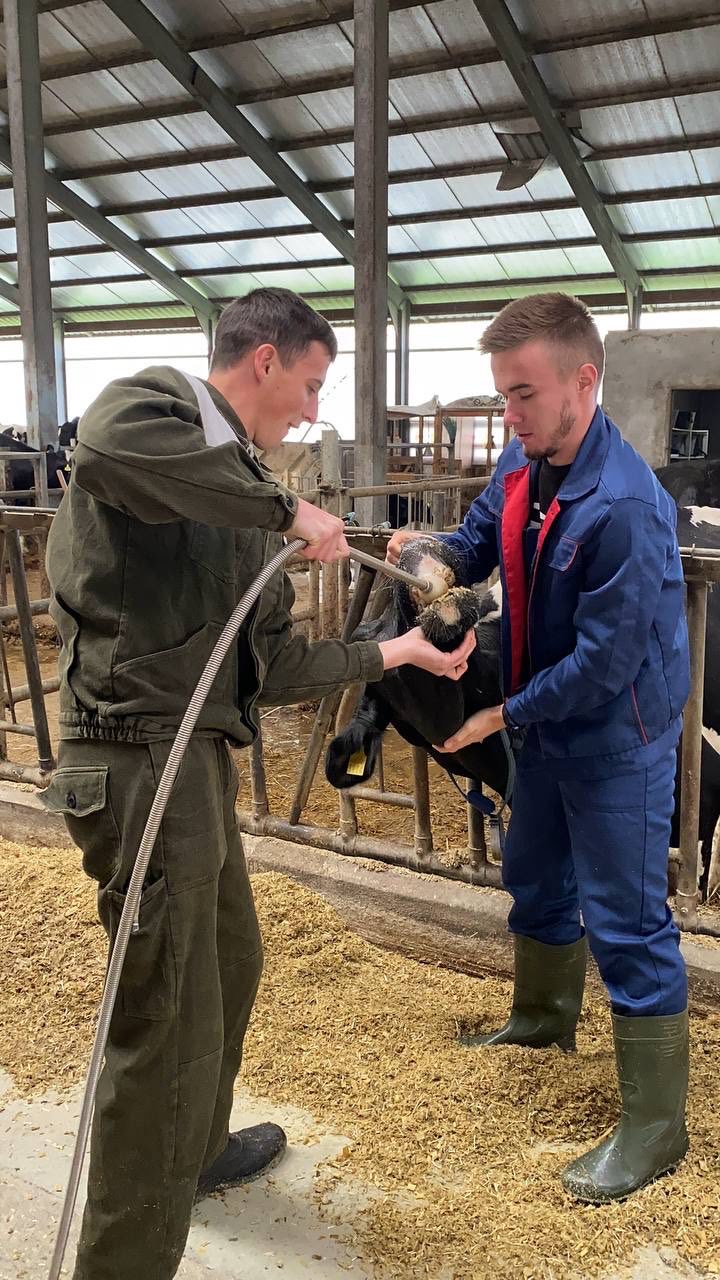
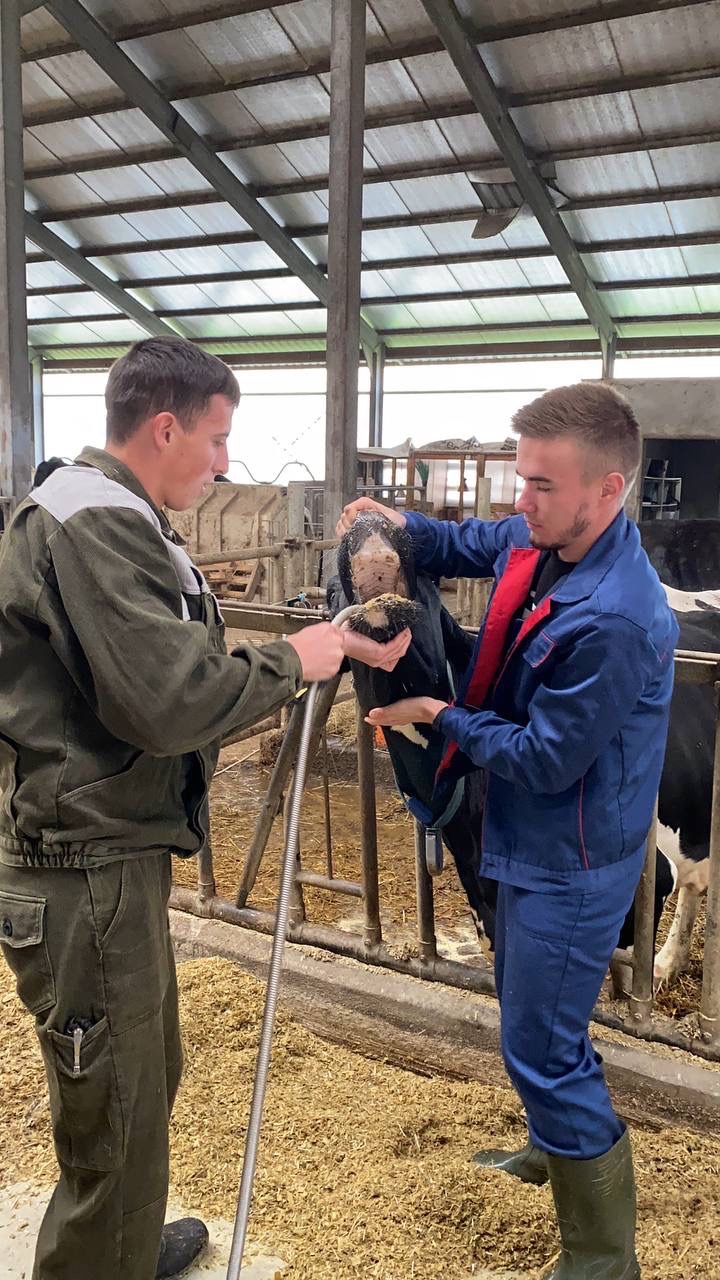
Students of the 5th year of study of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine undergo extramural clinical practice to acquire practical skills and competencies. The issue of animal reproduction is always relevant. Because it is both the output of offspring, and milk, and the repair of the herd. 09/28/2022 with PhD, assistant professor O. Yeroshenko, students underwent practical training in the conditions of the dairy farm of the Bila Tserkva National University, where they mastered the methods of diagnosing body condition in cows, obstetric and gynecological pathologies, and methods of animal therapy.
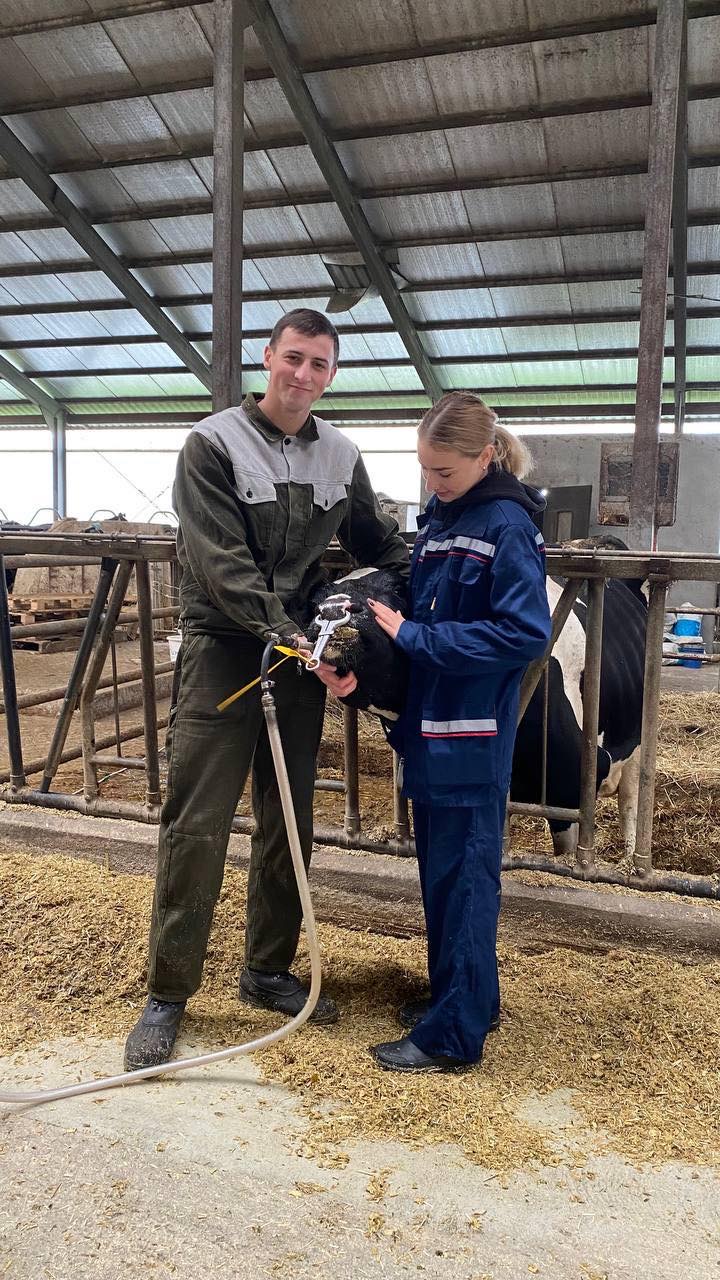
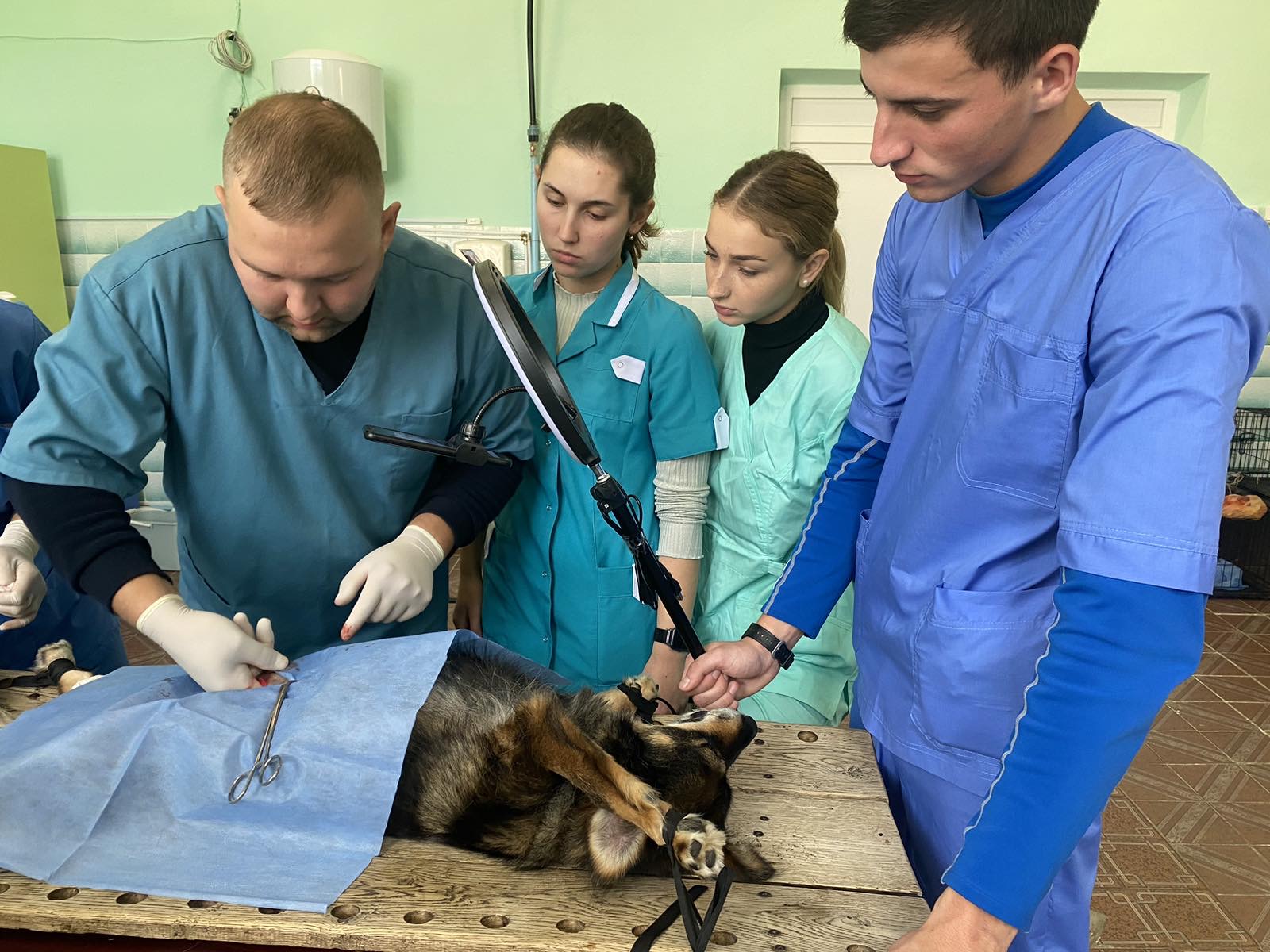
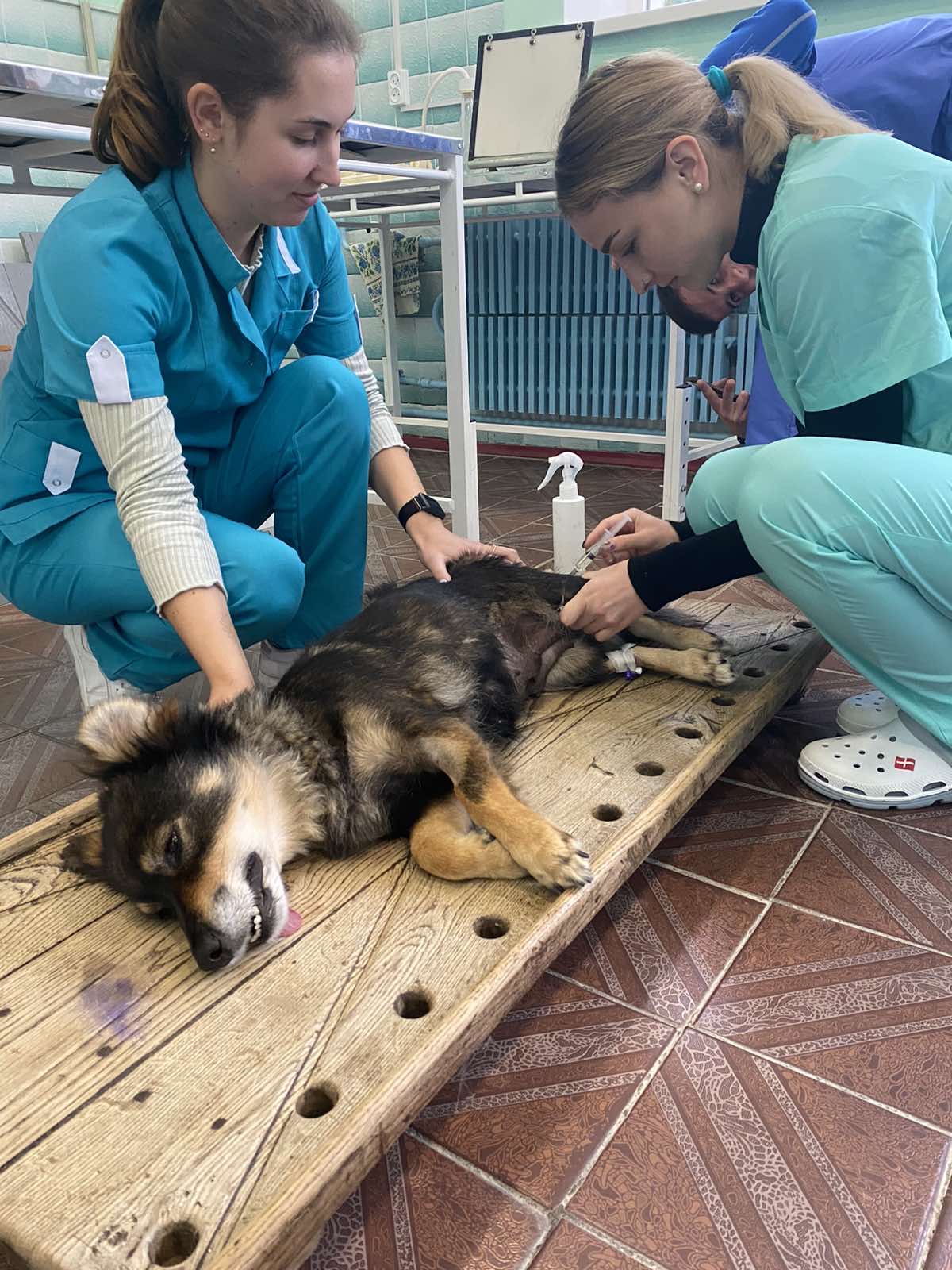
09/29/20 PhD, associate professor O.Chub with the students underwent practical training in the conditions of the "Terezine" dairy farm in the Vilna Tarasivka department, where they mastered various methods of administering medicinal substances, clinical examination of sick and healthy cows. On September 30, 2022, the students underwent practical training at the Interdepartmental Small Animal Clinic of the FVM with the PhD, assistant professor V. Chemerovsky of Department of Surgery and Diseases of Small Domestic Animals.